Directed Acyclic Graph
Acyclic: No Cycles
DFS in DAG
DFS with a clock preorder #, postorder
Pseudocode DFS:
DFS(G):
input: undirected or directed graph in adj. list
for all v in V, visited(v) = FALSE
clock = 1 # NEW STEP COMPARED TO UNDIRECTED GRAPH
for all v in V if not visited(v) then Explore(v)
Explore(w):
visited(w) = TRUE
preorder(w) = clock
clock++
for every edge out in E:
if not visited(z) then Explore(z)
post(w) = clock
clock++Example Run:
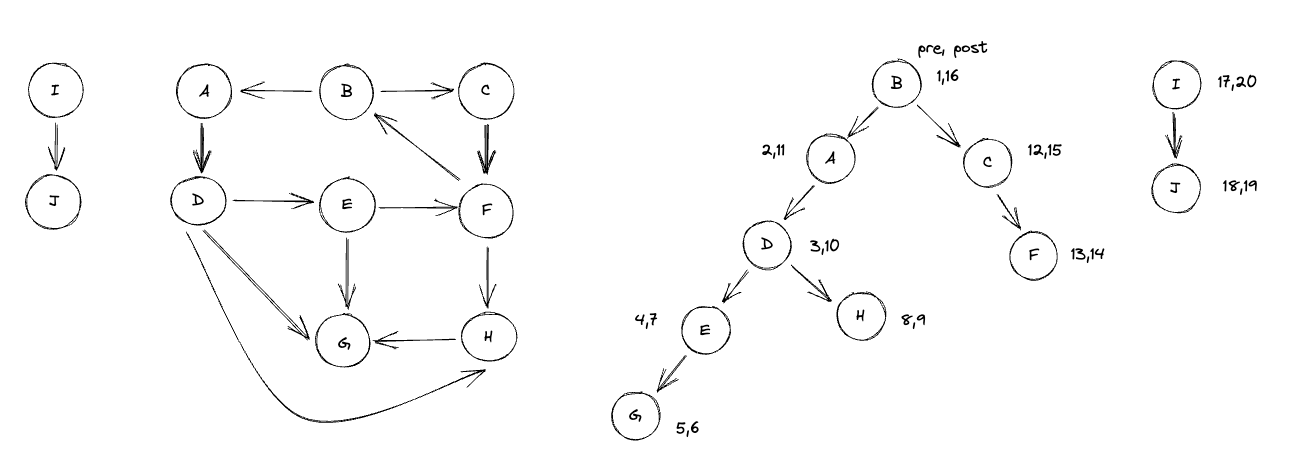
Classification of Edges
Given Edge
Forward
- post(v) > post(w)
- Ex: D G
- Pre(D) < Pre(G) < Post(G) < post(D)
Back:
- post(v) > post(w)
- Ex: F B, J I
- pre(B) < pre(F) < post(F) < post(B)
Cross:
- post(w) > post(v)
- Ex: F H, H G
- pre(H) < post(H) < pre(F) < post(F)
Key Claim:
Directed has a cycle IF AND ONLY IF its DFS tree has a back edge.
i.e If there are no cycles in a graph, then there are NO back edges in DFS tree.
Proof:
Suppose graph has 1 cycle, call it C =
Consider DFS, some vertex in C is visited first, call it . ’s subtree in DFS tree will equal every vertex reachable from and is not yet visited.
Suppose DFS tree has back edge .
How to detect if a graph is a DAG or not?
Run DFS and keep every pre / post #
Check every edge v w, see if back edge post(v) < post(w) then report a cycle.
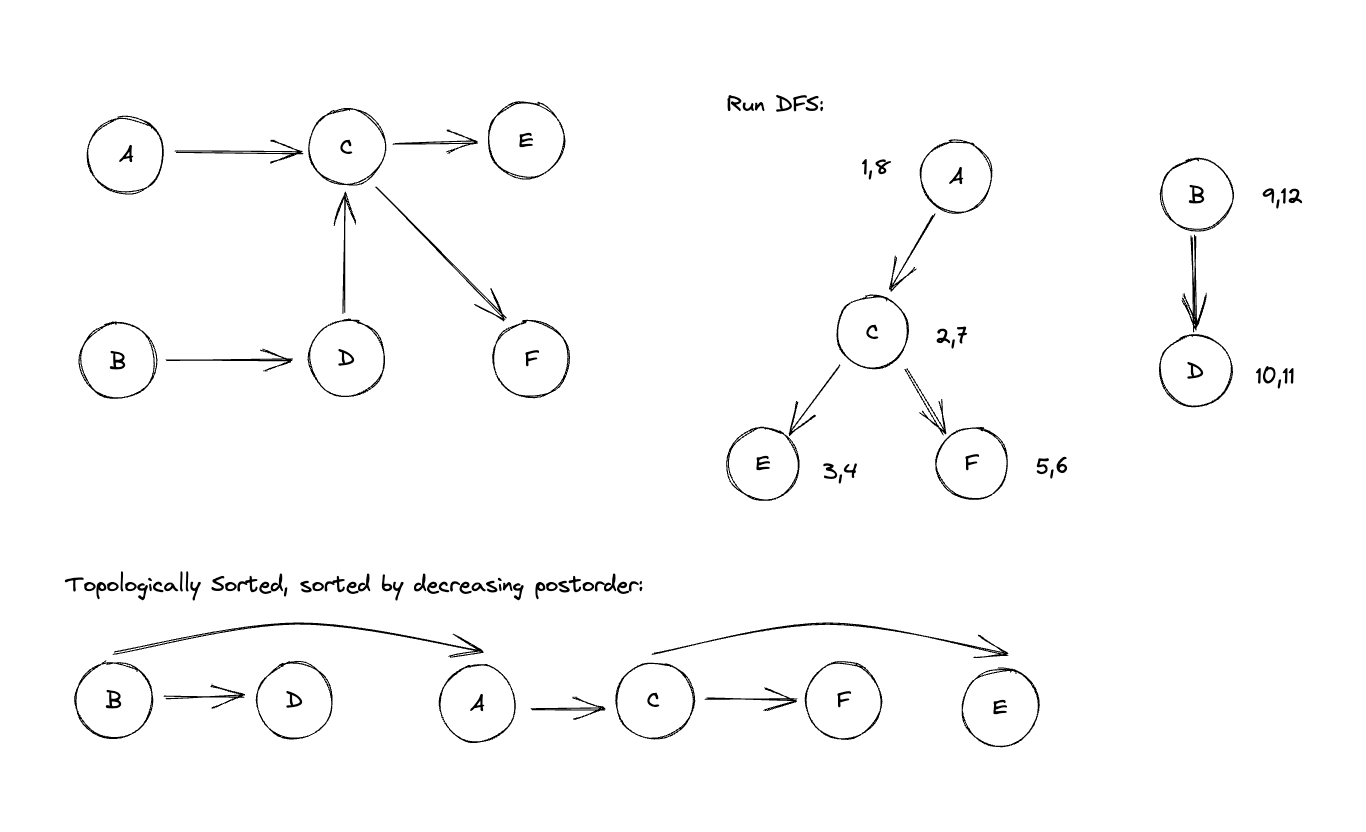
Topologically sort a DAG
Order vertices so all edges go left(earlier) to right (later).
Run DFS & order by post order #. Takes O(n + m) time.
Classification of Vertices
Source Vertex
- An vertex with no incoming edges
- In a DAG, there is guaranteed to have at least one source vertex
- Note that in a topologically sorted DAG, the leftmost vertex will be a source vertex.
Sink Vertex
- A vertex with no outgoing edges.
- In a DAG, there is guaranteed to have at least one sink vertex
- Note that in a topologically sorted DAG, the rightmost vertex will be a source vertex.
Arbitrary Directed Graph
Directed graph with arbitrary edges, cycles are allowed.
Strongly Connected
v & w are strongly connected if v w & w v.
Strongly Connected Components (SCC): Maximal set of strongly connected pairs
Goal: find SCC’s of arbitrary directed graph