Regression vs. Classification
Regression: Observe a real-valued input x and predict real-valued target y.
Classification: observe a real-valued input x and predict categorical/discrete target y
Examples of Classification Problems
Text Classification
- Classify the sentiment of a an online movie review (positive, neutral, negative)
Classification Example
MNIST Dataset (10 classes total): Classify 10 digits
To begin, let’s try a simple binary case: Differentiate 1 and 5.
- First, represent images to a real-valued input x (feature extraction)
- Possible Features:
- Raw number of pixels
- Strokes
- Symmetry
- After extracting features, you can draw a line to separate.
Note: represents and represents and .
Sigmoid Function
Sigmoid is defined as:
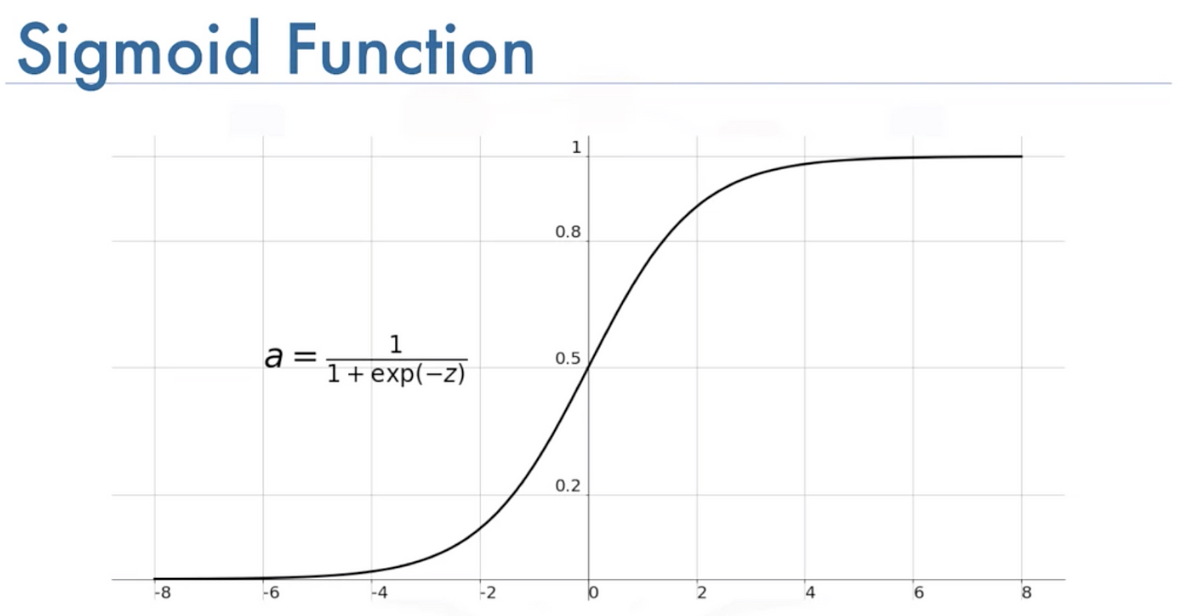 Note how Sigmoid(-z) relates
Note how Sigmoid(-z) relates
What makes Sigmoid Function Good?
- Our data is binary
- Our model is good if when and when
The Logistic Loss Function
The logistic loss function is the objective function:
It looks complicated but it is based on an intuitive probability interpretation and is easy to calculate.
The function will encourage the correct outputs from the Sigmoid function.
The Decision Boundary
In 2-d space, defines a line that separates the space. The loss function helps find the optimal w*.
Example: Find the Optimal w*
There is no analytical solution to this problem:
We must use gradient descent:
SGD for Logistic Regression
Initialize w(0) at step w = 0
for t = 0,1,2...:
Sample a batch of K data points
Let gradient = 0
for each sampled data (x, y)
gradient += -y x (sigmoid(w transpose * x))
w(t+1) = w(t) - step size * gradient
iterate until it is time to stop
end for loop
return the final parameters