Multi-Layer Neural Networks
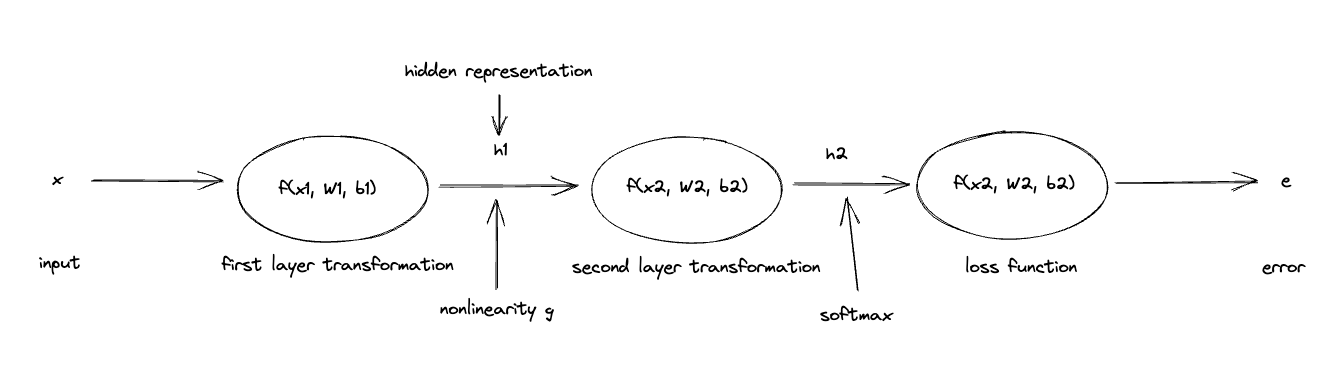
To train the network, we need to find the gradient of the error w.r.t the parameters (there are 4 in this example) of each layer, e.g. etc.
How do you calculate the gradients of each variable? Doing it by hand is extremely tedious, what happens if you want to change your model? Backpropagation is the solution.
Backpropagation
The key idea of backpropagation is to use chain rule on a computational graph.
Example
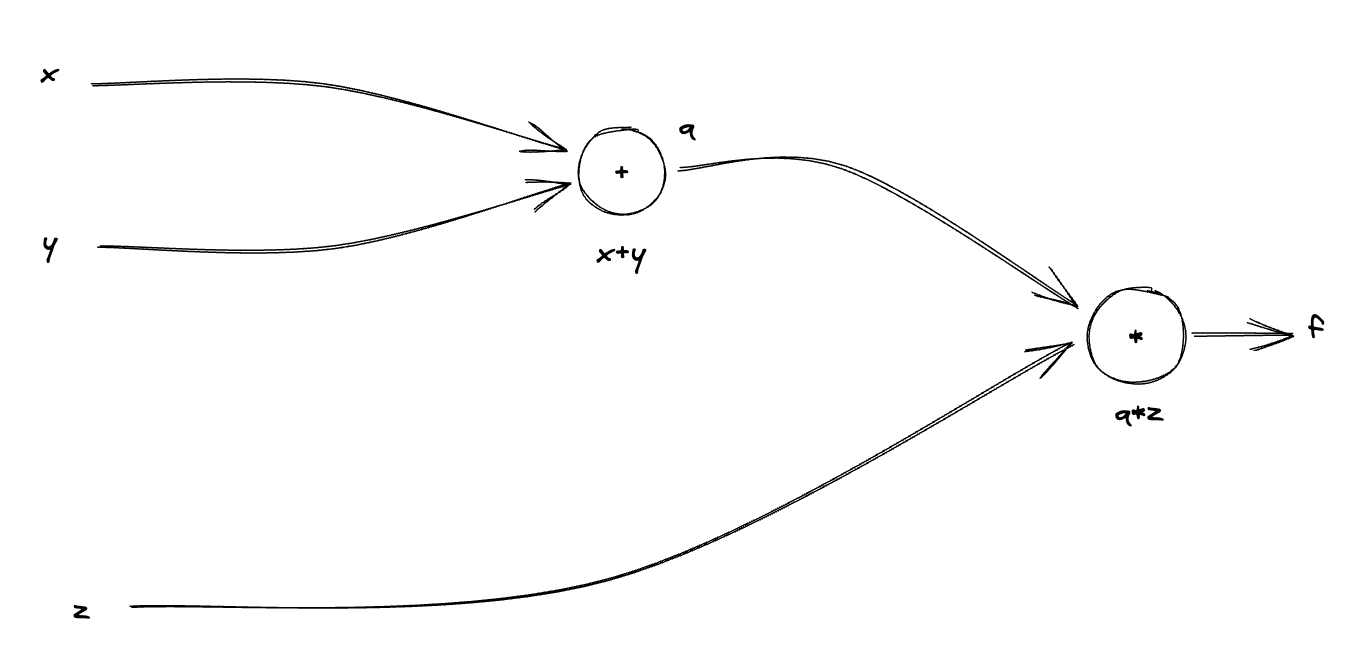
Given: We know that:
Here is the computational graph:
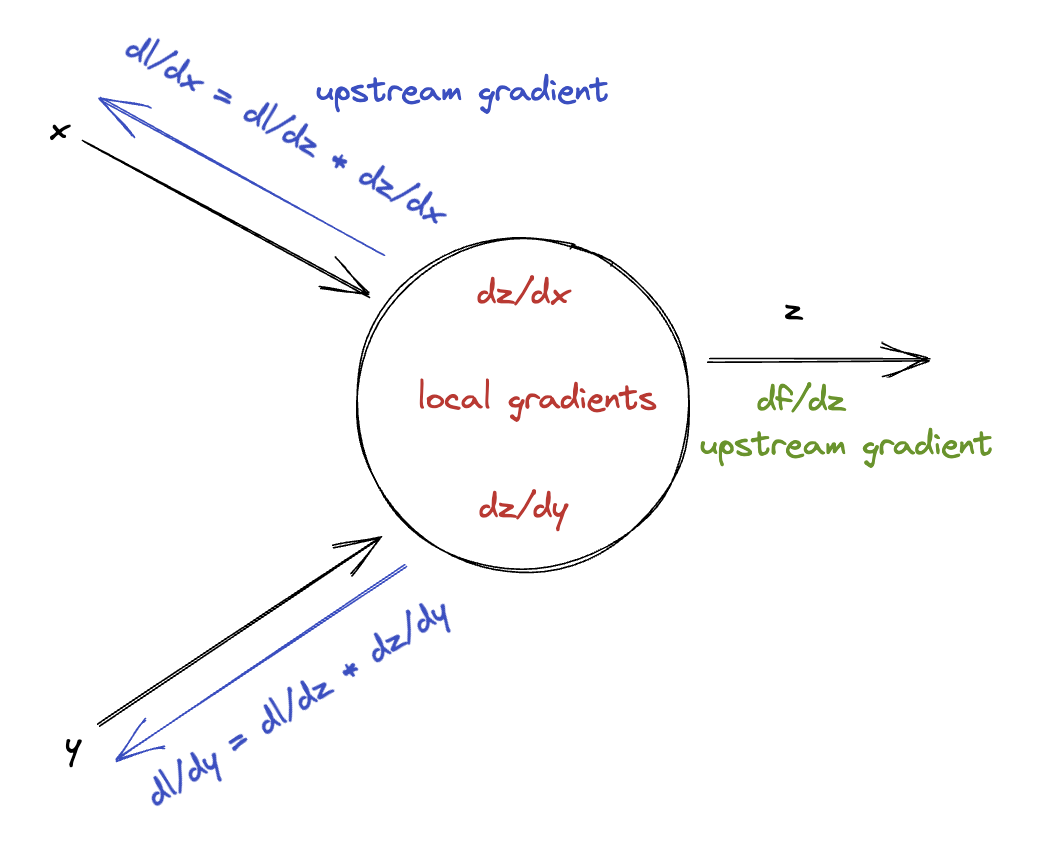
The way back propagation works is by working from the final layer and propagating backward by taking the upstream gradient and the local gradients and propagating backwards.
You can picture a node in the computational graph like this.
Midterm 1 Review
Three Portions:
- True or False, 6 Questions, 18 Points
- Multiple Choice, 8 Questions, 32 Points
- Major Questions, 3 Questions (Derivations / Short Answers etc.), 50 Points
Topics: XOR Problem (MUST REVIEW)
Multiclass Derivation
- Shape of each parameters
- Anything in Lecture 8 is fair game
Broadcasting in Python
Simple matrix and probability
- Understand the shape of the Matrix
- Shape of gradient
Probability (Bayes’ Rule)
Linear Regression
- Analytical Solution
- Be able to transform between to and explain how
- Know how to DERIVE analytical solution
Ridge Regression
- Know how to derive the analytical solution
- Are there any constraints to lambda (lambda must be positive, why? hint: think about minimizing meaning THERE WILL BE NO MINIMUM IF LAMBDA IS NEGATIVE)
Stochastic Gradient Descent / Gradient Descent / Optimization / Vector Calculus
- What is the definition of the gradient
- Remember, the gradient is always in the direction of the function increasing
- That’s how we minimize loss, we subtract the gradient
- How does learning rate affect gradient descent
- Too big? Overshooting, wild oscillation
- Too small? long time to converge
- Extremely big/small? flat
Difference between GD and SGD
- Gradient Descent will be smoother vs. SGD
- Initializations
- If the answer is convex, in the perfect case you will find the minimum
Logistic Regression
- Analytical VS Gradient Descent (gradient descent is right)
- Sigmoid()
- Decision rule for logistic regression
- Sigmoid() vs softmax() They are equivalent in the 2 class scenario
Multi-class
- In class derivative
- How will w update when given a certain input
- Softmax - There are special characteristics of the softmax function. If you can calculate the Softmax() where is a vector. Will the answer be the same as if you added a constant to every element of the Softmax. It will be the same. But if you multiply it will not be the same. From a numerical stability standpoint you want to subtract the greatest from every element of the softmax.
Python Coding
- Finding bugs
- Broadcasting shapes
FNN
- Nonlinearities AKA Activation Functions, why you need them
- Best choice is ReLu
-
- Note that if x is of dimension d, then W must be of dimension . Note that it has to be consistent with
- Overfitting vs Underfitting phenomenon
Notes: There will be no coding portion on the exam, you are only expected to perform multiple choice questions on coding. TWO QUESTIONS IN CODING