Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)
For a graph , for , is a subgraph of (Subset of edges).
A tree is a subgraph which is connected & acyclic.
A forest is a subgraph which is acyclic. (A tree is a type of forest)
MST = minimum spanning tree
Find a subgraph of minimum weight which is a tree (connected & acyclic)
Given a graph with for for :
MST problem: Given with for , find which is connected & minimizes . (We assume G is connected)
Example:
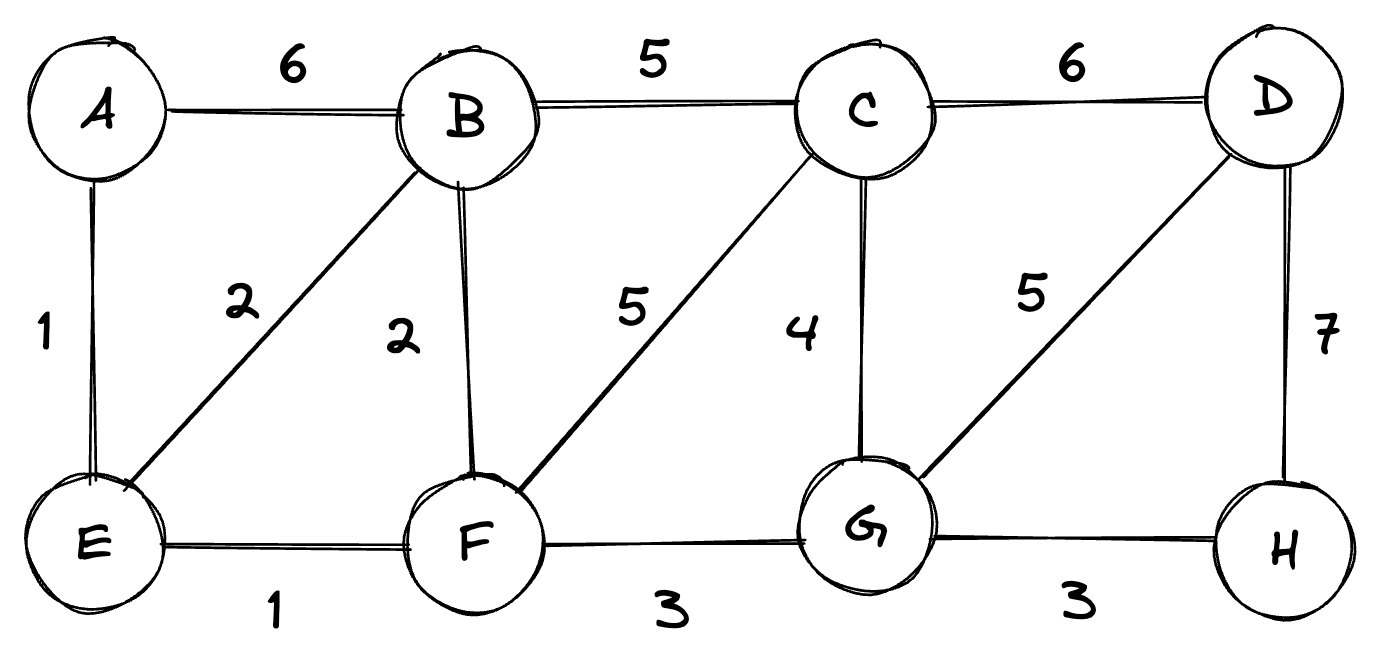
Weight of this graph is: ()
There are two possible MST’s, you could either use BF or BE.
Basic graph theory:
- Tree on n vertices has edges
- Any connected graph with exactly edges is a tree.
- In a tree there is exactly one path between every pair of vertices.
Prim’s Algorithm
T = partially explored set of vertices (arbitrary start) X = MST on T
for z not in T: cost(z) = min edge weight between z and T
next explored vertex: z not in X with min cost(z)
()
Prim(G,w):
input: undirected G = (V,E) with w(e) > 0
output: MST defined bby prev()
for all v in V
cost(v) = infinity
prev(v) = NULL
Choose any v in V to set to be s
cost(s) = 0
H = empty heap
For all v in V Insert(H, v, cost(v))
While H:
v = Delete Min(H)
For(V, z) in E:
if cost(z) > w(v,z) then:
cost(z) = w(v,z)
DecreaseKey(H, z, cost(z))
prev(z) = vKruskal’s Algorithm
Greedy approach try to add edge with minimum weight.
For input ,
- Sort E by increasing weight ( time by merge sort)
- Let X =
- Go through edges in increasing order of weight: for edge e = (y,z): if X e is acyclic then add e to X
Union-find data structure (Disjoint sets data structure):
- Maintain connected components in partial MST (v,x)
- To check if x union E is acyclic we check if y & z are connected in (v,x) Operations:
- MakeSet(x): create a new set just containing X )
- Find(x): return name of set containing x )
- Union(x,y): merge the sets containing x and y )
Krushkal (G,w):
For all z in V, MakeSet(z)
x = emptyset
Sort E by increasing weight
Go through E in increasing order
For edge e = (y,z):
if Find(y) != Find(z) then:
X = X union e
Union(y,z)
return xProof of correctness :
Cut property:
Krushkal’s — Why is it correct?
Proof of induction on |X|
Partial MST X on explored set S
Base Case: X is empty, S = {s},
Assume by induction that X is a partial MST on S that means there is a MST T on G where X T
Let be the next edge added to
We need to show: There is a MST where
This is implied by the following more general cut property