Language Modeling
During training, given the ground-truth words, predict word .
Example: Harry went back and saw Hermione
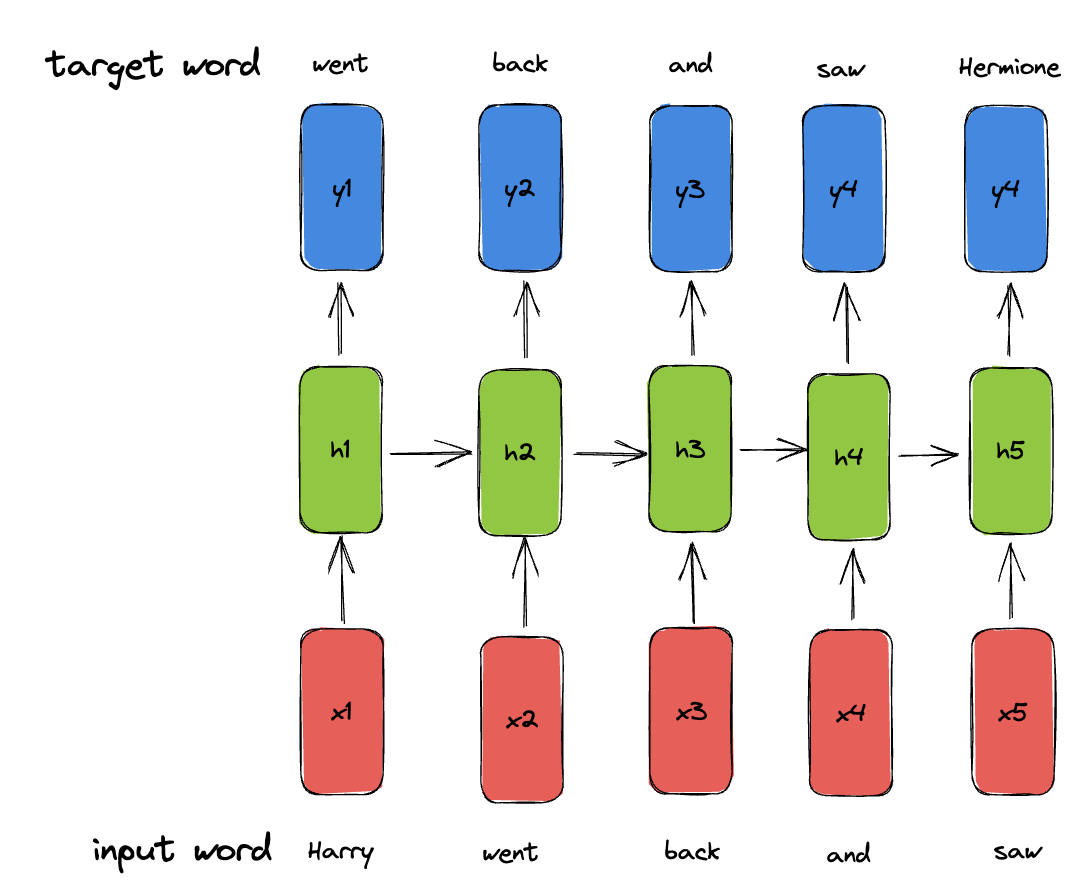
During inference, generate a new word each time and feed it back to the model.
Improved RNN Architecture
Recall the vanilla RNN recurrence formula.
Problems:
- vanishing / exploding gradients
- cannot model long-range dependencies
- difficulty with parallelization
There are architectures to alleviate these issues:
- Long short-term memory (LSTM)
- Gated recurrent unit (GRU)
They are still not enough to solve these problems:
- LSTM is still short term!
- Can’t model long sequences
Attention is All You Need
A revolutionary paper introducing the transformer architecture. 100,000 Citations in 7 years! Funnily used as a naming template for papers. (x is all you need)
Sequence to Sequence Generation
Seq2Seq generation has a wide variety of applications.
It can be used for machine translation, i.e English to Spanish, or even code generation, i.e English to Python.
Encoder-Decoder Paradigm
The encoder decoder paradigm takes in some input, encodes it, and then decodes it.
Step by Step Process:
- The encoder takes in some input, and outputs some context vector. This context vector could be or mean . It is flexible.
- The decoder is similar to language modeling, it takes as an input and outputs the result.
Problem: The context vector causes an information bottleneck because of the fixed-size vector.
Note
This paradigm is already outdated, newer language models are decoder only.
Seq2Seq with RNN and Attention
Generation at position :
- Compute Scalar importance score
- Normalize importance score to get attention weights
- Compute context vector as a linear combination of hidden states
- Compute context vector at each generation step
Transformer
Scaled Dot-Product Attention
Transformers use a different attention mechanism.
- The token attends to “we”, “are”, “eating”, and “bread”
Example:
Query:
- Keys: “we”, “are”, “eating”, and “bread”
- Values: “we”, “are”, “eating”, and “bread” Each word is represented by a vector: . will attend to four vectors, .
Instead of directly computing the similarity score between and the transformer incorporates a projection operation first.
Given that
- Project to query/key/value space
- Query:
- Key:
- Value: V =
- Computer the similarity score using the query and keys
Difference to RNN: Similarity score is calculated after projection
- Output the “context vector”
Difference to RNN: Context vector is also computed after projection